|
It seems that hardly a week passes without a disaster: worldwide heat waves, typhoons in Taiwan, flooding in Texas and West Virginia, wildfires in Canada and California, mudslides in Japan, tornadoes in the mid-west, terrorist attacks in Europe and the middle East, home-grown shooter attacks in Florida, etc. What is going on? Are disasters really increasing, and if so, why? Are "natural" disasters part of an earth cycle or are we causing them? It should come as no surprise that most definitions for disaster are at least somewhat anthropomorphic. The International Federation of Red Cross (IFRC) website defines a disaster as "...a sudden, calamitous event that seriously disrupts the functioning of a community or society and causes human, material, and economic or environmental losses that exceed the community's or society's ability to cope using its own resources." Disasters can be subdivided into five categories:
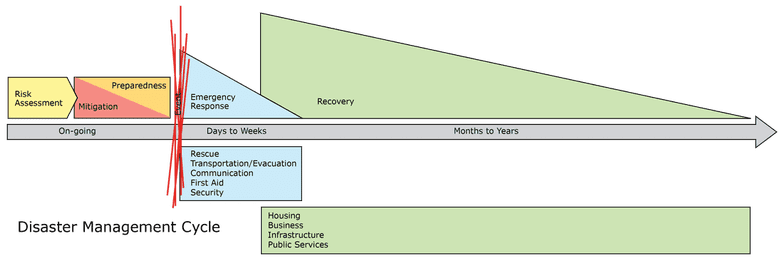
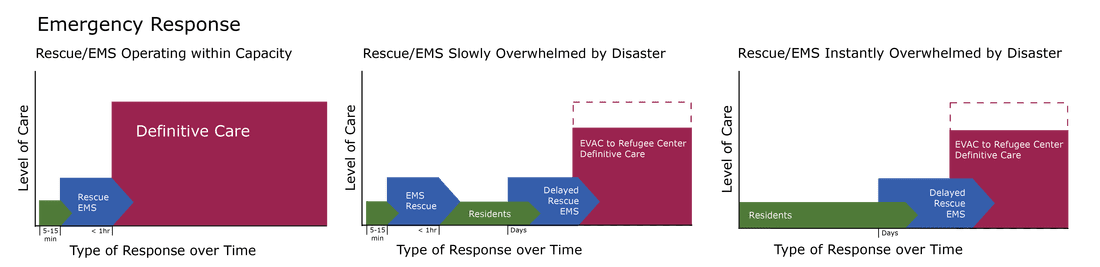
While the number of fatalities for some types of natural disasters—earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis—is decreasing due to better warning systems and preparedness on the part of residents, their communities, and state and federal governments, the number of people affected by them—via non-fatal injuries, loss of homes, businesses, and infrastructure—is larger due to population growth and expansion into disaster prone areas. Regardless of the type of disaster, the management cycle each community experiences before, during, and after a disaster is the same and can be represented by the following graphic: Risk Assessment The potential for many natural disasters can be predicted based on annual weather patterns, geologic conditions, and by using advanced technology; this gives residents, community, state and federal government an opportunity to prepare. And, as mentioned earlier, most industrial disasters can be prevented. Assessing risk and taking steps to mitigate and prepare for disasters minimizes fatalities should one occur and sets the stage for faster, and less expensive, physical and economic recovery. Mitigation & Preparedness Mitigation focuses on minimizing the damage should a disaster occur. Examples include reinforcing buildings to prevent collapse during an earthquake; fireproofing homes and property to increase the chance of protecting them during a wildfire; avoid building in flood plains; erecting and maintaining artificial reefs, levees, and dams for flood control; reestablishing natural buffer zones (mangrove stands, forests, and undergrowth) to reduce flooding, etc. Preparedness focuses on identifying refugee centers, having a emergency evacuation plan with potential disaster shelters (often a local school, community building, or parking garage), packing a Go-Bag, securing important documents (titles, insurance information including a list & photos of insured contents, passport, bank information, etc. online); seeking training in related rescue techniques and wilderness first aid; assembling personal and community first aid kits; having a reliable method to receive emergency alerts & updates; etc. Emergency Response In the immediate aftermath of a disaster local EMS and Fire/Rescue personnel responding to injuries or illnesses are often delayed or unavailable due a breakdown in infrastructure. Outside assistance from state, national, or international agencies is often required and takes days to mobilize (see graphics 2 & 3 below; the first graphic illustrates normal urban Rescue/EMS response times). In most disasters, the primary assessment and treatment of any injuries or illnesses is typically rendered by residents, often lay people, on the scene with care lasting until EMS and Fire/Rescue has been reestablished and the residents evacuated to definitive care or a disaster shelter, a process that typically requires days. In the wake of increasing disasters, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) has developed the Community Emergency Response Team (CERT) program that trains and registers residents interested in helping their neighbors/communities during a disaster. CERT members are recognized by, interact with, and fall under the formal EMS/Rescue incident command structure.
Disaster medicine is a sub-specialty of wilderness medicine where local Emergency Services are overwhelmed or become non-functional due to a natural disaster, terrorist attack, or infectious disease outbreak. It is similar to expedition medicine—another subspecialty of wilderness medicine—in that rescuers are called upon to aid patients with limited supplies, often under difficult environmental conditions, and where transport to definitive care is delayed for hours or days. It differs in that it involves a large number of patients, many who may be children, elderly, or suffering from a preexisting medical condition that limits their ability to respond to a developing situation effectively. If you are likely to be first on the scene after a disaster, consider seeking training in rescue techniques appropriate to the hazard in your geographic area and in wilderness/disaster medicine. Recovery It often takes years for affected communities to recover, especially if a significant number of homes, businesses, and infrastructure have been destroyed. Time and resources spent on mitigation and preparedness exponentially decrease the costs associated with emergency response and recovery, as well as shorten the time required for recovery. Information, Training, & Assistance The Department of Homeland Security, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), and the American Red Cross maintain websites with information and provide assistance with all aspects of disaster management cycle, including online training. A thorough web search will reveal additional sites and resources. Want more information on this and other wilderness medicine topics? Take one of our wilderness medicine courses. CERT members should consider our Wilderness First Aid or Wilderness First Responder course. Looking for a reliable medical field reference? Consider consider purchasing one of our print or digital handbooks; our digital handbook apps are available in English, Spanish, and Japanese. Updates are free for life. A digital SOAP note app is also available.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Categories
All
Our public YouTube channel has educational and reference videos for many of the skills taught during our courses. Check it out!
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
